How Long Do Late Payments Stay on Credit Report?

In the intricate world of personal finance, the significance of punctual payments often goes unnoticed until it unravels into a tangled web of consequences. At Sadek Law, we understand the paramount importance of timely payments, particularly in the context of credit scores and financial stability. In Philadelphia and beyond, the ramifications of late payments extend far beyond mere inconvenience. They are intricately intertwined with one’s creditworthiness and potential pathways to financial relief.
Delving into the complicated world of credit scoring, we explore how the simple act of missing a payment can have profound repercussions on your financial health. If you are a Pennsylvania or New Jersey resident who is struggling with debt or low credit scores, don’t hesitate to reach out. To schedule a free consultation with us, please call our office at 215-545-0008 today.
What Is a Credit Score?
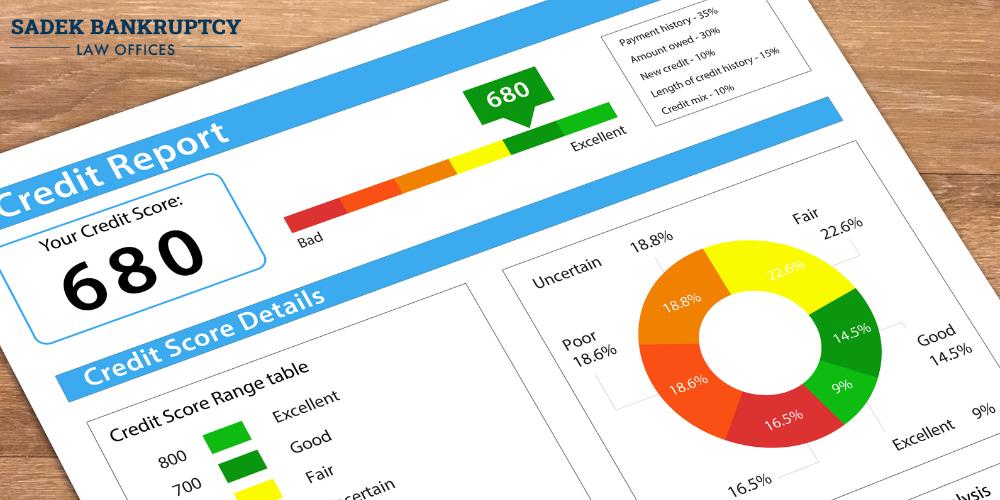
A credit score serves as a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness, providing lenders with a standardized metric to assess the risk associated with extending credit. It’s essentially a snapshot of a person’s financial health at a particular moment in time, distilled into a three-digit number.
This score influences the ability to secure loans, credit cards, mortgages, and other forms of credit, as well as the terms and interest rates attached to such financial products. Each credit bureau has its own way of evaluating your credit history and assigning a score. However, you can generally expect the following information to make up your credit score.
Payment History (35%)
Payment history holds significant importance, constituting roughly 35% of the score. This component reflects whether borrowers have consistently made on-time payments on their credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages. Late payments affect one’s score significantly. A history of late payments or defaults can significantly lower one’s credit score.
Amounts Owed (30%)
The amounts owed on credit accounts account for about 30% of the credit score. This factor considers the total debt owed, as well as the utilization rate—the ratio of credit card balances to credit limits. High utilization rates suggest a higher risk of default, which can negatively impact the credit score.
Length of Credit History (15%)
The length of credit history contributes around 15% to the credit report calculation. Generally, a longer credit history indicates a more stable financial track record, which can positively influence the score. Conversely, individuals with a limited credit history may have lower scores due to insufficient data for assessment.
Credit Mix (10%)
Credit mix, comprising about 10% of the score, evaluates the variety of credit accounts held by the individual. A diverse mix of credit types, such as credit cards, installment loans, and mortgages, demonstrates responsible credit management and can bolster the credit score.
New Credit (10%)
New credit accounts for approximately 10% of the score. This factor takes into account the frequency of credit inquiries and the opening of new credit accounts. Multiple inquiries or a sudden influx of new credit applications may signal financial distress or an increased risk of default, thus potentially lowering the credit score.
When Do Late Payments Show Up As Late on Credit Reports?

Late payments typically show up as late on credit reports when they exceed the grace period specified by the creditor. This grace period is usually around 30 days after the payment due date. Once this period elapses without the payment being made, the creditor may report the first missed payment to the credit bureaus, and it will then be reflected on the individual’s credit report. The severity of the impact may vary depending on the length of the delinquency and the individual’s overall credit history.
What Are Acceptable Reasons for Late Payments on Credit Report?
Acceptable reasons for late payments on a credit report typically include extenuating circumstances that are beyond the individual’s control, such as serious illness, sudden job loss, or natural disasters. Additionally, administrative errors or delays by the creditor or financial institution may also warrant consideration as valid reasons for any outstanding balance.
Do Partial Payments Count as Late?
Partial payments may not necessarily count as late, but they can still have adverse effects on credit reports depending on the creditor’s policies. While making partial payments can demonstrate a willingness to meet financial obligations, it’s crucial to understand that creditors typically expect full payment by the due date to avoid late fees and negative reporting to credit bureaus.
If the partial payment doesn’t cover the minimum payment required or if it’s not received by the due date, the creditor may still report the account as delinquent, potentially impacting the individual’s credit score.
How Does a Missed Payment Affect Your Credit Scores?
A missed payment can have significant negative effects on your credit scores. Payment history typically accounts for about 35% of your credit score, making it one of the most influential factors. When you miss a payment, it can lead to derogatory marks on your credit report, such as a late payment notation.
This can result in a decrease in your credit score, making it harder to qualify for new credit or obtain favorable terms on loans and credit cards. Additionally, the impact of a missed payment on your credit score may worsen over time if the delinquency remains unresolved or if further missed payments occur. The experienced attorneys at Sadek Law can help you better understand how late payments can impact your credit score.
What Happens If I Miss a Payment?
If you miss a payment on your credit account, the consequences can vary depending on how late the payment is.
Under 30 Days Late
If the payment is under 30 days past the due date, you may incur a late fee from the creditor, but it typically won’t be reported to the credit bureaus. However, it’s essential to make the payment as soon as possible to avoid further repercussions.
Over 30 Days Late
Once a payment is over 30 days late, the creditor may report the delinquency to the credit bureaus, which can negatively impact your credit score. This late payment notation will remain on your credit report for up to seven years, affecting your ability to qualify for new credit and potentially leading to higher interest rates on loans and credit cards.
Over 60 Days Late
If the payment is over 60 days late, the consequences become more severe. In addition to the negative impact on your credit score, the creditor may escalate their collection efforts, including contacting you more frequently and potentially taking legal action to recover the debt. Moreover, late payments beyond 60 days can significantly impair your creditworthiness, making it challenging to rebuild your credit in the future.
How Long Do Late Payments Stay on Credit Report?

Late payments can stay on your credit reports for seven years from the date of the missed payment. This negative notation can significantly impact your credit score and may affect your ability to qualify for new credit or obtain favorable terms on loans and credit cards during that time. Along with marks on one’s credit report, many individuals are also responsible for a late payment fee if they miss a payment.
How Long Do Collections Stay on Your Credit Report?
Collections accounts can stay on your credit report for up to seven years from the date of the original delinquency, regardless of whether the debt has been paid off or settled with the collection agency. This negative notation can have a significant impact on your credit score and may make it challenging to qualify for new credit or obtain favorable terms on loans and credit cards during that time.
How Long Do Closed Accounts Stay on Your Credit Report?
Closed accounts can stay on your credit report for varying lengths of time, typically seven to ten years from the date they were closed. The exact duration depends on the type of account and the credit bureaus’ policies. Closed accounts can still impact your credit score, particularly if they have a positive payment history, as this information contributes to your overall creditworthiness.
How Long Does Bankruptcy Stay on Your Credit Report?

Bankruptcy can stay on your credit report for up to ten years from the date of filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, or seven years from the date of filing for Chapter 13 bankruptcy. This negative notation can have a significant impact on your credit health.
It may make it challenging to qualify for new credit or obtain favorable terms on loans and credit cards during that time. However, the impact of bankruptcy on your credit score lessens over time, especially if you take steps to rebuild your credit responsibly.
How to Remove Late Payments from Credit Reports
Consumers can potentially remove late payments from their credit reports through a few methods. Before beginning, you can obtain free credit reports from the credit bureaus. First, they can contact the creditor directly to negotiate a goodwill adjustment, especially if the late payment was an isolated incident due to circumstances beyond their control. Additionally, disputing inaccurate late payments with the credit bureaus can lead to their removal if there are errors in reporting.
How to Avoid Late or Missed Payments
Consumers can avoid late or missed payments by setting up automatic payments or reminders through their bank or credit card issuer to ensure bills are paid on time. Creating a budget and tracking expenses can help individuals manage their finances more effectively, ensuring they have enough funds available to cover bills when they are due. It can also help keep each account current to avoid penalties.
Additionally, prioritizing payments and establishing an emergency fund for unexpected expenses can provide a financial safety net and reduce the likelihood of missed payments. Regularly reviewing credit card statements and bills for accuracy can also help promptly catch any discrepancies or unauthorized charges.
How to Improve Your Credit Score After a Late Payment

You can obtain a free credit score copy from each credit bureau. First, ensure all future payments are made on time to demonstrate responsible financial behavior. Paying off outstanding debts and reducing credit card balances can also have a positive impact on credit utilization ratios.
Additionally, regularly monitoring credit reports for errors and disputing inaccuracies can help ensure an accurate reflection of creditworthiness. Building a positive credit history over time by responsibly managing credit accounts and diversifying credit mix can improve credit scores. Practicing patience and persistence while adhering to these strategies can gradually lead to a healthier credit profile.
Contact Sadek Bankruptcy Law Offices Today
As you navigate the complexities of managing your finances, it’s crucial to recognize the profound impact that late payments can have on your credit score. At Sadek Law, we understand the challenges and frustrations of dealing with credit issues, including late payments and their repercussions.
Our experienced team is dedicated to guiding you through the intricacies of credit repair and financial recovery, offering personalized solutions tailored to your unique circumstances. Whether you’re facing the aftermath of late payments or seeking comprehensive debt relief strategies, we provide the support and expertise you need to achieve a brighter financial future.
Don’t let late payments define your creditworthiness—reach out to Sadek Law today and take the first step towards a fresh start.





